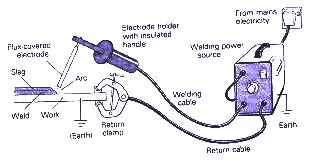
 |
| Flux Shielded Metal |
It is the arc welding process wherein coalescence is produced by heating the w/p with an fsmw electric arc set up between a flux coated electrode and the w/p.
The flux covering decomposes due to arc heat and performs
many functions like arc stability weld metal protection etc.
Electrons liberated from the cathode move towards the anode and the arc accelerated. When they strike the anode at high velocity, a large amount of heat is generated.
(Heat required for welding is obtained from the arc
struck between a coated electrode and the w/p). The arc temperature and thus the arc heat
can be increased or decreased by employing a higher or lower arc current.
The arc melts the electrode end and the job. Material
droplets are transferred from the electrode to the job, through the arc and are deposited
along the joint to be welded.
The flux coating melts, produces a gaseous shield and
slag to prevent atmospheric contamination of molten weld metal.
Flux Shielded Metal Construction:
Before welding, the edges of the workpieces are
suitably prepared. The edges and the area adjoining them are cleared
of all the scale, rust, dust, etc. either chemically
or mechanically, using a cure brush grinding wheel, etc.
The workpiece to be welded arc is positioned and spaced
concerning each other and held in a fixture.
Welding leads are properly connected to the power source and the workpiece power source is switched on and a suitable welding current is set. The electrode is gripped in the holder and the operator is ready for the weld. Before welding on the actual structure, it is always better to try on a scrap piece to ascertain the optimum current.
Flux Shielded Metal Working:
In manual metal are welding arc between the
electrode and the w/p is generally stuck either by momentarily touching by scratching
the electrode on the job in the arc of the circle.
Once the arc has been established and the arc length adjusted, the electrode is inclined to an angle of approximately 20 with the vertical. To achieve a comparatively deeper penetration electrode angle with the vertical is further reduced. The electrode is progressed along the joint at a constant speed. This is necessary to maintain a constant arc gap. The bead width can be increased by employing higher arc current, lower arc travel speed.
Flux Shielded MetalAdvantage :
1) Arc welding is the
simplest of all welding processes.
2) The equipment is portable
and the cost is fairly low.
3) A big range of metals and their alloys be
welded.
4) Welding can be carried out at any position with the welding quality.
Flux Shielded Metal Limitations
1) Because of the limited length
of each electron and brittle flux coating its mechanization is difficult.
2) The process uses a stick
electrode and thus it is slow as compared to MIG welding.
3) Because of the flux coated
electrode, the chances of slag entrapment and other related defects are more as
compared to Mig or tig welding.
Flux Shielded Metal Application
a) Air receiver, tank, boiler.
b) Shipbuilding.
c) Pipe and Penstock jointly.
d) Building and bridge
construction.
e) Automobile and Aircraft
industry etc.







0 Comments
Leave a Reply...