 |
| tungsten inert gas |
TIG welding process wherein coalescence is produced by heating the job with an electric arc struck between a tungsten electrode and the job. Shielding gas is used to avoid atmospheric contamination of the molten weld pool.
Tungsten Welding Operation:
Welding current, water, and inert gas supply are turned on, and the arc is stuck either by touching the electrode with scrap metal.
The arc is then struck between the electrode and precanceled job to be welded.
The welding torch is brought near to the job. When the electrode tip reaches a distance of 3 to 2 mm from the job, a spark jumps across the air gap between the electrode and the job. The air path gets ionized and the arc is
established.
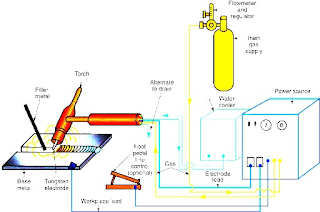
TIG welding Construction and Working
Welding current, water, and inert gas supply arc turned
on. The arc is
struck either by touching the electrode with scrap metal
or then breaking by increasing the arc length. The procedure was repeated twice or
thrice warming up the tungsten electrode. The arc is then struck between the
electrode and precanceled job to be welded. This method avoids breaking the
electrode tip, job contamination, and tungsten loss.
When the electrode tip reaches a distance of 3 to 2 mm from a job a
spark jumps across the air gap between the electrode and the job. The air
path gets ionized and the arc is established. After
striking the arc, it is allowed to impinge on the job
and a molten weld pool is created. The welding is started by moving the torch
along the joint as in oxyacetylene welding. At the far end of the job, the arc is broken by increasing the arc length. The shielding
is allowed to impinge on the solidified weld pool for a few seconds even after
the arc is extinguished. This will avoid atmospheric contamination of the weld metal.
TIG welding Advantage
1) No flux is used, hence there is
no danger of flux entrapment.
2) Because of the clear visibility
of the arc and the job, the operator can exercise better control of the welding process.
3) This process can weld in all
positions and produce smooth and sound welds with fewer spatters.
4) Tig welding is very
much suitable for high-quality welding of thin materials.
5) It is a very good process
for welding nonferrous metals.
TIG welding Disadvantage
1) Under a similar application MIG
welding is a much faster process as compared to TIG welding, since TIG welding
requires a separate filler rod.
2) Tungsten if it transfers to a molten weld pool can contaminate the same.
Tungsten inclusion is hard and brittle.
3) Filler rod end if it by chance
comes out of the inert gas shield can cause weld metal contamination.
4) Equipment costs are higher than those for flux-shielded metal welding.
TIG weldingApplication
1) Welding aluminum, magnesium, copper
2) Welding sheet metal
and thinner sections.
3) Welding of expansion bellows, transistor cases, can seats, etc.
4) Precision welding in atomic energy, aircraft
chemical, and instrument industry.
5) Rocket motor chamber fabrication in launch vehicles.







0 Comments
Leave a Reply...